Detail Content
Financial Advisors
A Financial Advisor (FA) has a crucial role in selecting and screening qualities of companies to be listed in the Stock Exchange of Thailand. An FA is obligated to ensure that the companies disclose thorough, accurate and sufficient information for investors in making decisions. An FA is required to provide opinions to shareholders in cases that the listed companies involve in significant transactions that could affect rights and interests of the shareholders such as mergers and acquisition transactions, related party transactions, and acquisition or disposal of assets transactions. Obviously, FAs' performance has a significant bearing on investors and stakeholders on a broader scale.
Regulatory Summary
Duties
Performing the duties with accountability, using knowledge, competency, experience, prudence and care in carrying out the tasks professionally;
Upholding professional code of ethics;
Preparing working paper which must be maintained as a record for a minimum of 3 years;
Reporting to the SEC of any non-cooperation cases of the clients. Failure to report to the SEC will be deemed FAs' flaws, inappropriateness, or deficiencies in performing the duties.
FAs may resort to information from a specialist, having verified that the person is truly knowledgeable and competent in that field.
FAs shall have a supervisor, who was approved by the SEC, co-sign to certify completeness of information provided in the applications, filings, reports and all document submitted to the SEC.
Scope of works
1. Issuance and Offering for Sale of Securities
Working with issuers of securities in preparing and submitting applications, filings, prospectus and other documents to the SEC and in certifying the accuracy, completeness of the information provided primarily based on the interests of the investors;
Providing opinions that the issuers are qualified for approval by the SEC;
Educating, advising issuers of securities about duties, responsibilities, relevant rules and related procedures;
Where there are estimates, FAs shall render opinions on reasonableness and feasibilities of the assumptions employed in preparing the estimates;
Taking actions to ensure that neither the executives of securities issuers nor any FAs disseminate the information that is not contained in the filing;
Together with the issuers, clarifying to the SEC the following occurrences when arising within one year ( for Thai issuing companies), and three years ( for foreign issuing companies) from the effective date of the filing; (A) the issuers change the operation significantly ; (B) the issuers use the proceeds from the sale of securities not in line with the declared objectives, or not complying to the provision under section 81 (of the Securities and Exchange Act regarding reporting results of the sale of securities) or (C) the issuers are not complying to the conditions or obligations required for approval as disclosed in the filing.
Clarifying, in conjunction with the issuers, to the SEC in the cases that the actual operating results are significantly different from the estimate.
2. Acquisition of securities for business takeover
- As tender offer preparer
Jointly with the tender offerors, preparing a tender offer and related documents as required.
Studying the information of the tender offerors and other relevant information to get thorough understanding; taking actions to ensure that the information furnished in the tender offer are correct, complete, not misleading to the users of the information, and that no information could affect the decisions of the securities holders of the undisclosed business.
Appraising the value of non-cash consideration provided by the tender offerors in exchange for the securities;
Rendering opinions to the securities holders of the business to be acquired if the tender offeror can fulfil the proposed plans, and if the proposal is justifiable.
Not conspiring with the tender offeror in covering up any information about the actual tender offeror.
Taking actions to ensure that the tender offeror recognizes the duties and responsibilities in acquisition of securities for business takeover.
- As advisor of shareholders
Two types of advisory tasks; as for a tender offer and for a whitewash waiver
For a tender offer
Providing opinions on the tender offer for securities and other documents required;
Analyzing and assessing financial positions and the operational results of the business activities, as well as impacts on the shareholders, to come up with recommendations for the shareholders to accept or to reject the tender offer, based on the principle of the best interests of the securities holders of the business;
Identifying advantages/disadvantages if the shareholders reject the tender offer, in case of a tender offer by a company that is delisting from the stock exchange.
For a whitewash waiver
Providing opinions to the shareholders regarding the application for a waiver from making a tender offer;
Reviewing to comprehend the assumptions, policies and operational plans of the waiver applicant to be able to render opinions to shareholders regarding the reasonableness and feasibility of such policies and operational plans;
Analyzing and assessing impacts of the waiver application with regards to the rights and interests of the shareholders, and ensuring the completeness of the information which could impact shareholders' decision making;
Reviewing fairness of the pricing of new shares that the listed companies plan to offer to the waiver applicants;
Carrying out due diligence on name lists, number of shares, voting right number of those persons, and of the concert party having the duty to report their holdings together with those of the waiver applicant as required under sections 246, 247 of the Securities and Exchange Act;
The number of voting rights that the waiver will obtain after acquiring the securities and will gain in addition in the future without triggering the obligation to make a tender offer for all securities of the listed companies.
3. Other cases
Independent FA (IFA)'s opinions are mandatory on the following issues:
Characteristics and details of the related party transactions;
Rationalities and benefits of the transactions;
Objectives and justifications in making the transactions;
Comparisons for advantages and disadvantages for the companies in various dimensions for entering into/not entering into the transactions;
Comparisons for advantages and disadvantages of entering into related party transactions vs. transactions with an outside party.
Fairness of pricing and conditions for transactions:
Expressing views to the shareholders if they should vote for or against the transactions, supported by justifications, assumptions and relevant factors.
- Acquisition and disposition of assets
An IFA's opinions on the following issues are compulsory:
Reasonableness and benefits of the transactions to the company;
Fairness of pricing and conditions of the transactions;
Rendering opinions on whether the shareholders should vote for or against the transactions, given the supporting reasons.;
Sufficiency of working capital of the listed companies, in the case that the listed company or subsidiary company is on backdoor listing.
Disclosure on reasonableness of the transactions should address at the minimum the following issues:
|
- Conditions for transactions
|
- Causes of a conflict of interest
|
|
- Doing Business in the Future
|
Approval for Financial Advisors and Supervisors
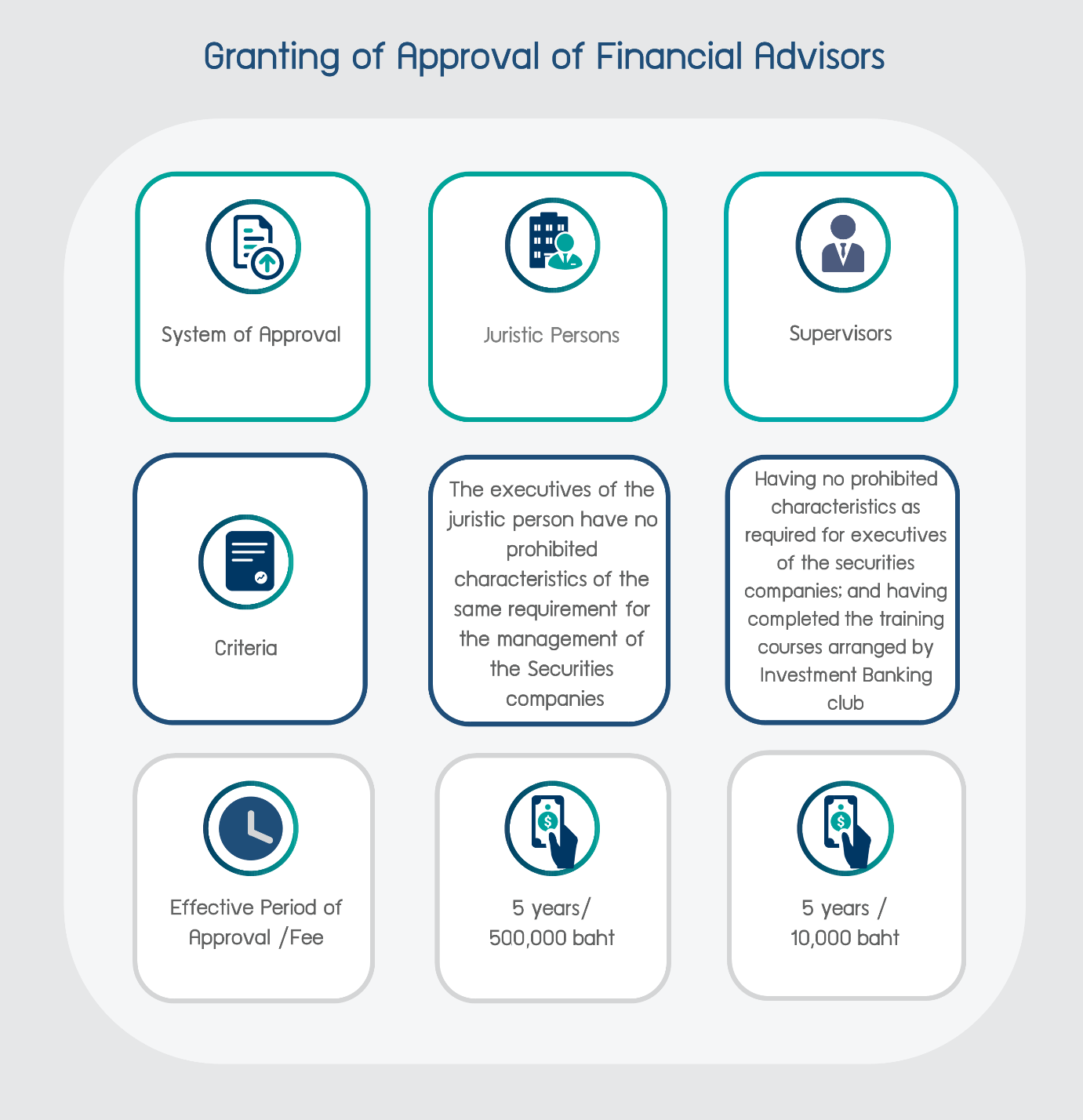
Juristic Persons
|
(1) Being a financial institution or a juristic person established under Thai law with a main objective of undertaking the business of financial advisor, accounting advisor or legal counselor;
|
(2) Having a specific work unit with a discrete performing function of financial advisory;
|
(3) Having operational rules and guidelines of financial advisory functions which are precise, reliable, secure and sufficient in accordance with the professional standards and ethics;
|
(4) Having no prohibited characteristics specified such as having actions that indicate a lack of professional ethics or standard of conduct in performing the duties of financial advisor.
|
(5) Directors, managers, the executives of the investment banking unit adhering to professional code of ethics of financial advisor, integrity, and commitment to going-concern business; having understanding and public accountability; having no prohibited characteristics such as being under receivership, bankrupt, incompetent or quasi-incompetent by a court order;
|
(6) Having at least one full-time supervisor who shall be an approved person by the SEC;
|
(7) Being a member of the Investment Banking club.
|
Supervisors
|
(1) Having qualifications and no prohibited characteristics as required for the executives of the financial advisory unit;
|
(2) Having passed the tests/training courses conducted by the Investment Banking club
|
Independence of Financial Advisors
FAs require independence to effectively perform the duties. The criteria for consideration of independence include the followings:
FAs' holding shares of an issuer who is a listed company must be less than or equal to 5%.;
FAs shall not hold shares of an issuer who is not a listed company, except for the case of over 2 years of holding the shares at less than or equal to 5%;
An issuer/ major shareholders/director of the issuer must hold shares in FA less than or equal to 5% (in case of holding each other's shares but not exceed the total of 10%);
Directors/managers/head of investment banking unit/supervisors/officers of the investment banking unit shall not be the same person as directors of the issuer except for being ID/AC of both issuer and FA.
FAs shall not be a related party/have a conflict of interests to be deprived of independence.
Related Handbooks and Guidelines
The Investment Banking Club
The SEC
Related Rules and Regulations
The Notification of the Office of the Securities and Exchange Commission Concerning Granting of Approval of Financial Advisors and Their Scope of Work
The Notification of the Office of the Securities and Exchange Commission No. SorChor. 36/2546 Re: Rules for the Application for a Waiver from the Requirement to Make a Tender Offer for All Securities of the Business by Virtue of the Resolution of the Shareholders' Meeting of the Business
The Notification of the Board of Governors of the Stock Exchange of Thailand Re: Disclosure of Information and Other Acts of Listed Companies Concerning Connected Transactions, 2003 Clause 20(5)
The Notification of the Board of Governors of the Stock Exchange of Thailand, Re: Disclosure of Information and Other Acts of Listed Companies Concerning Acquisition and Disclosure of Assets, 2004
Related Forms
Application for Approval of Financial Advisors (Form FA-1)
Application for Approval of Supervisors for Financial Advisors (Form FA-2)
Report on Changes or Addition of Directors/Managers/ Department Managers or Equivalent and Higher in Charge of Financial Advisory Function/ Supervisors (Form FA-3)